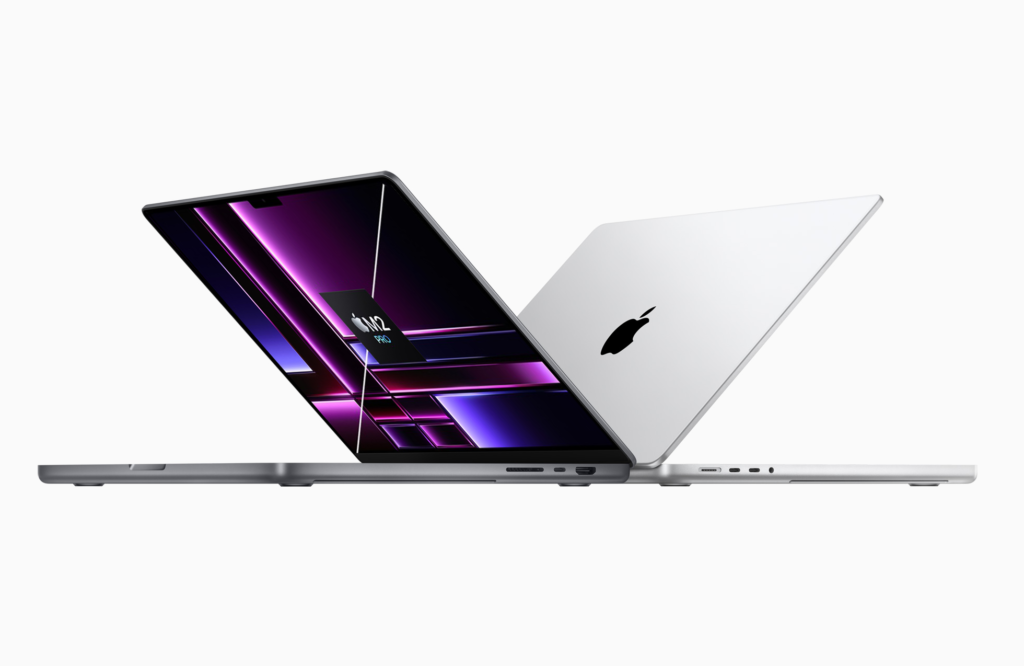
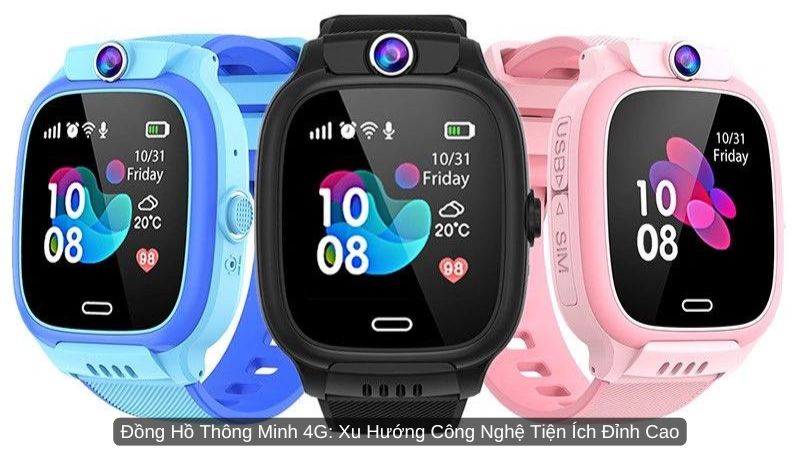
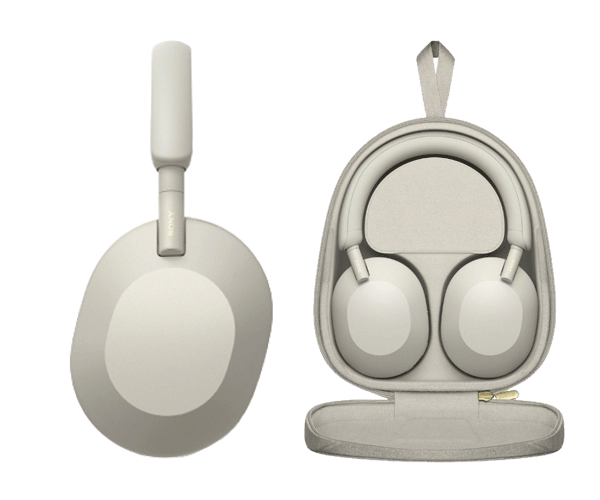
Máy tính và Phụ kiện
Generate About Us Content
Generate Your About Us Content
Between 1971 and 1984, Kahneman and Tversky had published a series of quirky papers exploring the ways human judgment may be distorted when we are making decisions in conditions of uncertainty. When we are trying to guess which 18-year-old baseball prospect would become a big-league all-star, for example. To a reader who is neither psychologist nor economist (i.e., me), these papers are not easy going, though I am told that compared with other academic papers in their field they are high literature. Still, they are not so much written as constructed, block by block. The moment the psychologists uncover some new kink in the human mind, they bestow a strange and forbidding name on it (“the availability heuristic”). In their most cited paper, cryptically titled “Prospect Theory,” they convinced a lot of people that human beings are best understood as being risk-averse when making a decision that offers hope of a gain but risk-seeking when making a decision that will lead to a certain loss. In a stroke they provided a framework to understand all sorts of human behavior that economists, athletic coaches, and other “experts” have trouble explaining: why people who play the lottery also buy insurance; why people are less likely to sell their houses and their stock portfolios in falling markets; why, most sensationally, professional golfers become better putters when they’re trying to save par (avoid losing a stroke) than when they’re trying to make a birdie (and gain a stroke).